In a world where personal data is constantly at risk, self-sovereign identity offers a new approach to protecting and managing our digital identities.
Understanding self-sovereign identity
Self-sovereign identity is a concept that gives individuals full control over their own digital identities. This means that individuals are the ultimate owners of their personal data and can choose who to share it with.
Using blockchain technology and public-key cryptography, self-sovereign identity allows for secure and **verifiable credentials** that can be shared in a **peer-to-peer** manner without the need for a central authority. This decentralization provides greater privacy and security for users.
By storing identity information on a **distributed ledger**, individuals can have more control over their personal data and who has access to it. This technology can help prevent data breaches and identity theft by giving users the power to manage their own identities.
Evolution of digital identity
By moving away from centralized databases and adopting a **peer-to-peer** network, self-sovereign identity allows for greater privacy and security. Through the use of **public-key cryptography** and **digital signatures**, users can verify their identity without the need for a third-party identity provider.
Verifiable credentials play a key role in this system, allowing individuals to securely store and share their digital identity information. This approach not only enhances security but also improves user experience by giving individuals more control over their personal data.
Problems with centralized digital identifiers
Centralized digital identifiers pose several problems when it comes to security and privacy.
One major issue is the risk of a single point of failure, where a breach in the centralized system could compromise the entire network. This puts user data at a high risk of theft or manipulation.
Additionally, centralized systems often require users to trust a single entity to manage their identity, which goes against the principles of self-sovereign identity. Users should have full control over their own personal information without having to rely on a third party.
Furthermore, centralized systems are susceptible to censorship and manipulation by those in control, leading to potential discrimination or exclusion of certain individuals.
To address these issues, self-sovereign identity solutions leverage **blockchain** technology to create a secure, decentralized network where individuals have full ownership and control over their identity data. This ensures greater privacy, security, and autonomy for users.
Benefits of self-sovereign identity management
Self-sovereign identity management offers individuals the freedom and control to manage their own digital identities without relying on centralized authorities. This empowers users to securely manage their personal information and choose who has access to it, increasing privacy and security.
By utilizing digital signatures and distributed ledgers, self-sovereign identity management ensures the integrity and authenticity of identities, reducing the risk of data breaches and identity theft. This decentralized approach also enhances user trust and reduces the reliance on third-party identity providers.
Furthermore, self-sovereign identity management enables individuals to easily verify their identities across various platforms and services, simplifying the authentication process. This not only improves user experience but also enhances security by reducing the need for sensitive information to be shared.
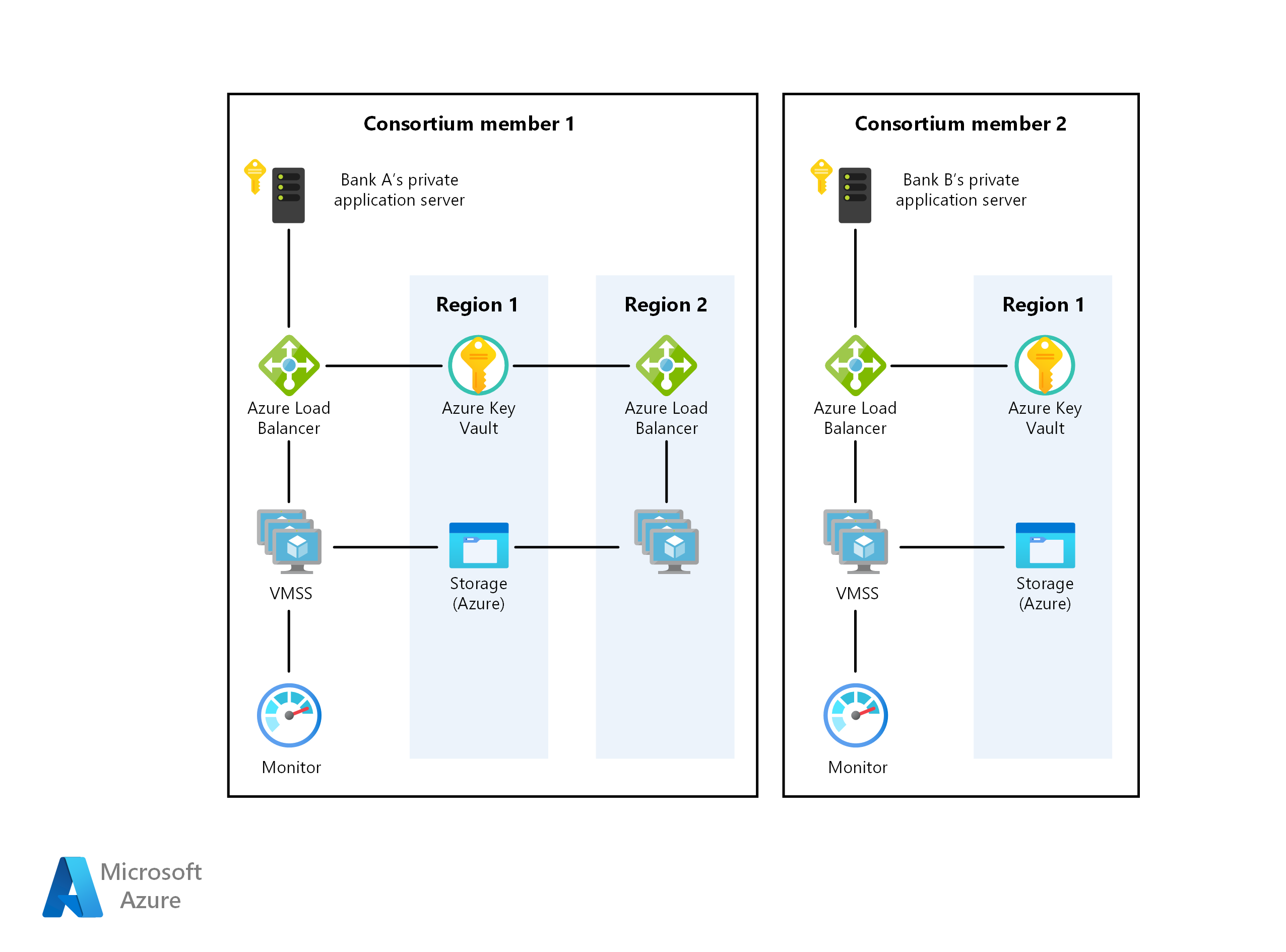
SSI Pillar 1: Blockchain
SSI Pillar 1: **Blockchain** is a foundational element of Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI), providing a secure and decentralized way to manage digital identities. By utilizing a **distributed ledger**, SSI allows individuals to have control over their own personal information, reducing the risk of data breaches and identity theft.
With SSI, users can create **digital credentials** that are stored on the blockchain, ensuring tamper-evident technology and secure verification and validation processes. This technology enables the creation of **decentralized identifiers** (DIDs), which can be used across various platforms and services without the need for a central authority.
By adopting SSI, individuals can have greater ownership and control over their personal identity, reducing reliance on third-party identity providers such as Google or Facebook. This shift towards a more user-centered design approach aligns with best practices outlined by organizations like the World Wide Web Consortium and the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency.
SSI Pillar 2: Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs)
SSI Pillar 2 focuses on Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs), which are a crucial aspect of Self-Sovereign Identity. DIDs provide a way to create unique identifiers that are controlled by the individual, rather than a centralized entity. This decentralized approach enhances security and privacy, as users have more control over their personal information.
By using DIDs, individuals can securely manage their digital identities across various platforms and services. This technology enables the verification and validation of credentials without relying on a single identity provider. DIDs also support the concept of user-centered design, putting individuals in charge of their online identities.
When considering SSI and DIDs, it’s essential to prioritize cybersecurity and follow best practices to safeguard personal information. Embracing decentralized identifiers can help protect against data breaches and enhance the overall security of digital identities. Organizations like the World Wide Web Consortium and the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency promote the adoption of DIDs for a more secure and user-centric online experience.
SSI Pillar 3: Verifiable Credentials (VCs)
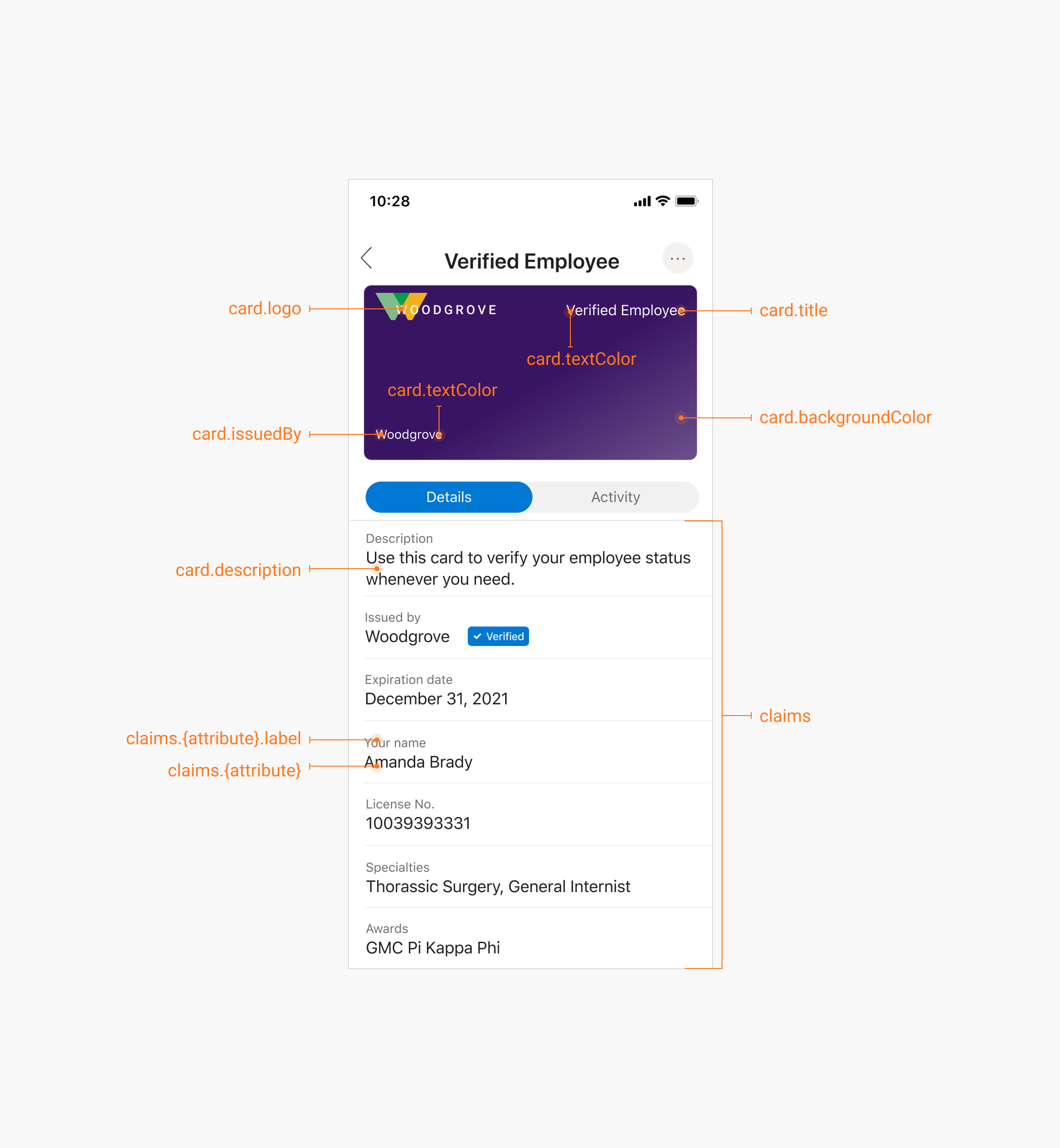
In Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI) Pillar 3, Verifiable Credentials (VCs) play a crucial role. VCs are digital credentials that can be **shared** and **verified** without the need for a centralized authority. This decentralized approach enhances security and privacy by giving individuals control over their own **identity**.
With VCs, users can securely store and present their credentials, such as a driver’s license or passport, on a **computer network**. These credentials are **protected** with a digital signature and contain metadata to ensure their **authenticity**. This innovative approach reduces the risk of **data breaches** and identity theft.
By using VCs, individuals can interact online without revealing unnecessary personal information. This technology is revolutionizing the way we **authenticate** ourselves in a digital world. Organizations like the United States Department of Homeland Security and Okta, Inc. are embracing VCs as a best practice for **identity verification**.
Instant credential verification benefits
![]()
Instant credential verification offers numerous benefits, including increased security and efficiency in verifying identities. With self-sovereign identity, individuals have more control over their personal information and can easily verify their credentials without relying on third parties. This reduces the risk of identity theft and fraud, as users can securely store and share their credentials through digital signatures and metadata.
By utilizing self-sovereign identity, individuals can streamline the process of proving their identity in various online interactions, such as accessing secure websites or logging into social media accounts. This eliminates the need for cumbersome identity documents and reduces the risk of identity theft. Furthermore, the use of self-sovereign identity helps protect against data breaches and unauthorized access to personal information.
Self-sovereign identity wallet
By using a self-sovereign identity wallet, users have more control over their personal information and can choose when and how to share it with others. This helps to protect against identity theft and data breaches, as users can determine who has access to their information.
One key feature of a self-sovereign identity wallet is the use of **decentralized identifiers**, which are unique identifiers that are not controlled by any single entity. This helps to ensure the security and privacy of the user’s information.
Self-sovereign identity use cases
Self-sovereign identity has a wide range of use cases across various industries. One common application is in the realm of digital identity verification, where individuals can securely store and manage their personal information without relying on centralized authorities. This technology is particularly useful in scenarios where traditional identity documents may be prone to fraud or data breaches.
Another use case for self-sovereign identity is in the realm of online authentication. By utilizing digital signatures and secure communication protocols, individuals can prove their identity online without the need for passwords or other vulnerable forms of authentication. This can help mitigate the risk of identity theft and unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Furthermore, self-sovereign identity can also be used to streamline processes such as KYC (Know Your Customer) verification, supply chain management, and secure access to services. By leveraging decentralized identifiers and tamper-evident technologies, organizations can ensure the integrity and authenticity of digital transactions.
Self-sovereign identity standards
By utilizing technologies such as digital signatures and decentralized identifiers, self-sovereign identity systems enable individuals to prove their identity across various online platforms without relying on centralized authorities. This not only enhances security and privacy but also reduces the risk of identity theft and fraud.
With the rising concerns over data breaches and privacy violations, self-sovereign identity standards offer a promising solution for individuals looking to take control of their online identities.
Creating a self-sovereign identity
Protect your self-sovereign identity by implementing tamper-evident technology and secure communication protocols. Be cautious about sharing personal information on social media or other online platforms, as this can put your identity at risk. Consider using a mobile app or digital wallet to store and manage your credentials securely.
By taking these precautions and following best practices for identity management, you can safeguard your personal information from threat actors and potential data breaches.
Additional resources and references
You may also find it helpful to explore materials on digital signatures, communication protocols, and decentralized identifiers to enhance your knowledge further.
Additionally, articles on best practices in personal identity protection and case studies on data breaches can provide valuable insights into the importance of self-sovereign identity.
For those looking to delve deeper into the technical aspects, resources on machine-readable passports, digital watermarking, and secure channels can be beneficial.
Keep in mind that staying informed on the latest developments in the field, such as advancements in blockchain technology or decentralized identity solutions, is crucial for enhancing your understanding of self-sovereign identity.



