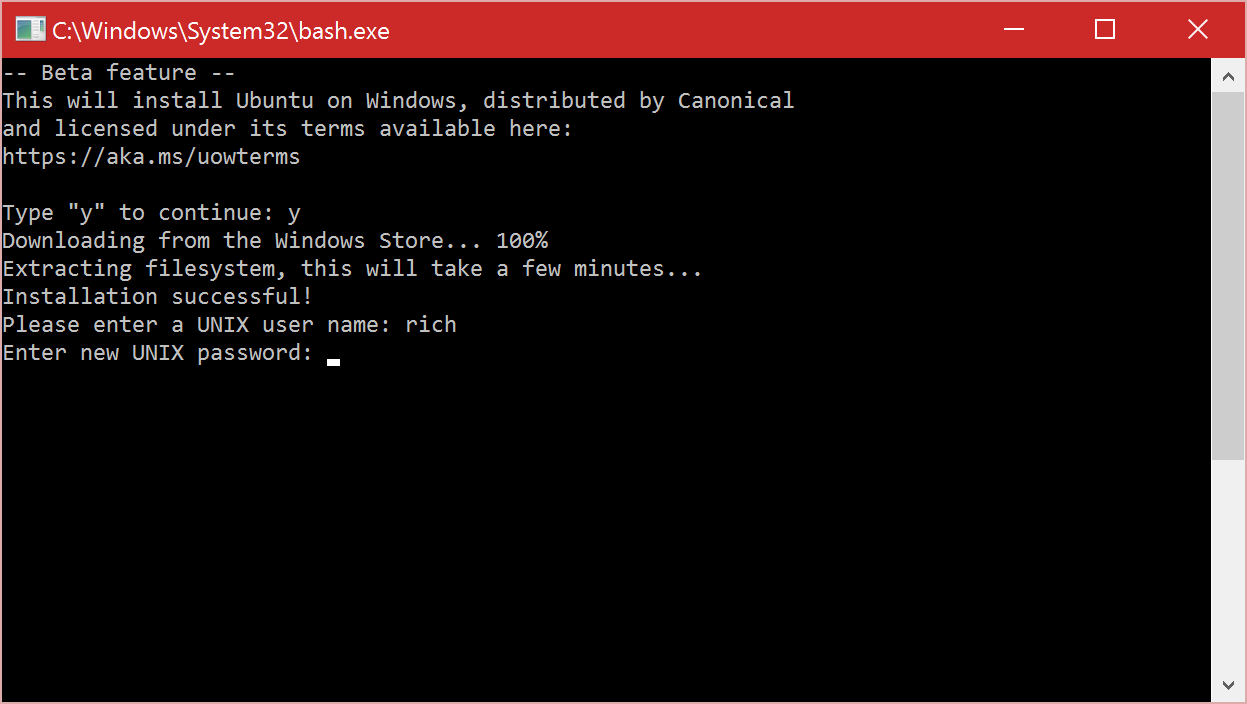
Welcome to the world of Linux! In this article, we will explore the basics of Linux for beginners, covering everything from navigating the command line to understanding file systems. Let’s dive in and unlock the power of this versatile operating system.
Mastering Linux Command Line
In this Linux course for beginners, you will learn the essentials of mastering the Linux Command Line. This crucial skill will allow you to navigate and interact with your Linux operating system effectively.
Understanding commands, file systems, and basic scripting will be covered in this course. You will also learn about package managers, software repositories, and Red Hat Certification Program if desired.
By the end of this course, you will have the knowledge and skills needed to work as a system administrator or Linux expert. This training will provide a solid foundation for further learning and experience in the world of Linux.
Whether you are looking to manage a personal computer, a data center, or a server, this course will set you on the right path. Start building your Linux skills today and open up new opportunities in the world of technology.
Linux Server Management & Security

Understand the basics of **Linux** distributions and how to navigate the **command-line interface**.
Discover how to utilize the **package manager** to install and update software efficiently.
Master essential skills such as **system administration** and **file system** management for a secure server environment.
Enhance your knowledge of **security** measures like **Secure Shell** and **authorization** to protect your server from potential threats.
Gain hands-on experience through practical exercises and tutorials to solidify your understanding.
Start your journey towards becoming a proficient **Linux** user with our comprehensive course.
Learning Linux in 5 Days
In this Linux Course for Beginners, you will learn how to navigate the Linux operating system in just 5 days. By the end of this course, you will have a strong understanding of the Linux file system, package manager, and command-line interface.
You will also gain hands-on experience with basic Linux commands, text editors, and **shell scripting**. This course is designed for beginners with no prior experience in Linux, making it perfect for those looking to start a career as a system administrator or **Linux expert**.
Throughout the course, you will have access to tutorials, lectures, and practical exercises to reinforce your learning. Upon completion, you will be well-prepared to take the next step, whether it’s pursuing a **Red Hat Certification** or diving deeper into Linux distributions.
Don’t miss this opportunity to kickstart your Linux journey and acquire valuable skills for **automation, troubleshooting**, and **server administration**. Join today and take the first step towards becoming a Linux pro.
Linux Administration Bootcamp
Learn essential skills such as **troubleshooting**, **automation**, and **data communication** to become proficient in Linux administration. Our comprehensive curriculum covers everything from basic commands to advanced concepts, ensuring you have a solid foundation in Linux.
By the end of the course, you will be equipped with the knowledge to pursue certifications like the **Red Hat Certification Program** and work confidently with Linux servers. Take the first step towards becoming a Linux expert and enroll in our beginner-friendly Linux course today.
Open Source Software Development with Linux and Git
Learn the fundamentals of Linux through this beginner’s course. Understand the basics of Linux distributions and how it differs from Microsoft Windows. Gain hands-on experience with shell scripting and utilizing secure shell (SSH) for remote access. Dive into *software repository* management and version control using Git.
Explore the power of open-source software development with Linux and Git. Master essential concepts like *data compression* and *data communication*. Develop your skills in text editing and scripting languages like Bash. Learn how to navigate the Linux environment efficiently and work with computer files effectively.
Enhance your understanding of Linux through practical tutorials and real-world examples. Build a strong foundation in Linux development to achieve your goals in the tech industry. Don’t miss out on this opportunity to expand your knowledge and expertise in open-source software with Linux and Git. Start your Linux journey today!
Linux Tutorials and Projects
In this **Linux Course for Beginners**, you will find a variety of **tutorials** and **projects** to help you get started with **Linux**. From basic commands to more advanced topics, this course is designed to provide a solid foundation for those new to the **Linux** operating system.
You will learn how to navigate the **Linux** **shell** efficiently, manage **software repositories**, and set up a **web server** using **WordPress**. Additionally, you will gain experience using a **text editor** for **editing** files and writing **scripts**.
By the end of this course, you will have the skills needed to work with **Linux distributions** and perform tasks such as **scheduling** **jobs**, **data compression**, and **user authentication**. Whether you are using a **personal computer** or managing a **data center**, this course will help you achieve your **Linux** learning **goals**.
Red Hat Enterprise Linux Overview
Red Hat Enterprise Linux is a popular **Linux distribution** used in many **server** environments. It offers a stable and secure platform for running **web servers**, **software repositories**, and other critical services.
Understanding how to navigate and work with Red Hat Enterprise Linux is an essential skill for anyone looking to work in **server administration** or **software development** roles. This **Linux course for beginners** will provide you with the foundational knowledge needed to start working with this powerful operating system.
Topics covered in this course include **shell scripting**, **software installation**, **file management**, and **user authentication**. By the end of this course, you will have the skills needed to navigate the **Linux command line**, edit files using a **text editor**, and manage **permissions** and **security** settings on a Linux machine.
Whether you are looking to expand your **IT skills**, build a **web server**, or simply learn more about **open-source** operating systems, this Linux course will provide you with the knowledge and tools needed to succeed. Dive into the world of Linux and start building your expertise today.
Building Core Linux Skills
If you’re looking to **build core Linux skills**, then a Linux course for beginners is the perfect starting point. This course will cover essential topics such as navigating the **shell** and understanding how to work with **software repositories**.
You’ll also learn about **Linux distributions** and how they differ from other operating systems like **Microsoft Windows** or **Mac**. Understanding concepts like **scripting languages** and **hard links** will be crucial in mastering Linux.
By the end of the course, you’ll be able to confidently navigate the Linux environment, write basic scripts, and manage files efficiently. This foundational knowledge will set you on the path to becoming proficient in Linux and open up opportunities for further learning and exploration.
Validating and Expanding Linux Skills
When it comes to **validating** and **expanding** your **Linux skills**, taking a **Linux course for beginners** is a great way to achieve that. These courses are designed to help individuals who are new to Linux understand the basics and build a strong foundation for further learning.
In a Linux course for beginners, you can expect to learn about **Linux distributions**, **shell commands**, **software repositories**, and more. These courses often cover topics such as **scripting languages**, **file management**, and **server configurations** to give you a well-rounded understanding of Linux.
By enrolling in a Linux course for beginners, you can gain the **authorization** to access and manipulate files, run programs, and perform other tasks on a Linux system. This hands-on experience is crucial for anyone looking to work with Linux in a professional capacity.
Whether your **goal** is to work as a **system administrator**, **developer**, or simply enhance your **technical skills**, a Linux course for beginners can provide you with the knowledge and confidence you need to succeed in the world of Linux.
Red Hat Learning Subscription
By enrolling in this course, you will learn how to create and manage computer files, utilize scripting languages like Bash, and explore the world of open-source software. The curriculum includes tutorials, lectures, and hands-on exercises to help you grasp key concepts and develop practical skills in Linux.
With the guidance of experienced instructors, you will gain the knowledge needed to work with servers, perform scheduling tasks using Cron, and understand the power of hard links. This course is designed to support your learning journey and empower you to achieve your goals in mastering Linux.
Whether you are a Mac user looking to expand your skills or someone interested in the world of programming, this Linux course for beginners is a valuable resource for anyone seeking to enhance their technical knowledge. Take the first step towards becoming proficient in Linux with this engaging and informative course from Red Hat Learning Subscription.
Classroom and Virtual Training Options
Classroom training provides a more traditional learning experience with face-to-face interaction with instructors and classmates. This can be beneficial for those who prefer a structured learning environment and thrive on in-person interactions. Virtual training, on the other hand, offers the flexibility to learn from anywhere with an internet connection. This option is ideal for those who prefer self-paced learning or have busy schedules.
Regardless of which option you choose, Linux Course for Beginners ensures that you receive high-quality training from experienced instructors. The course covers all the essential concepts of Linux, including navigating the shell, managing software repositories, and scripting with Bash. Whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to expand your knowledge, this course is designed to help you achieve your learning goals.
By enrolling in Linux Course for Beginners, you’ll gain valuable skills that can benefit you in various areas, such as server administration, web development, and programming. With a focus on hands-on learning and practical exercises, you’ll be well-equipped to tackle real-world challenges. Don’t miss this opportunity to kickstart your Linux journey and take your skills to the next level.
Best Introductory Linux Courses for Beginners
1. Udemy offers a great course called “Linux for Beginners,” which covers the basics of the Linux operating system in a clear and easy-to-understand way. This course is perfect for those who are new to Linux and want to learn the fundamentals.
2. Another popular option is the “Introduction to Linux” course on Coursera. This course is created by the Linux Foundation and provides a comprehensive introduction to Linux, including topics such as the command line, file systems, and package management.
3. If you prefer a more interactive learning experience, Linux Academy offers a “Linux Essentials” course that includes hands-on labs and quizzes to help reinforce your learning. This course is designed for beginners and covers essential Linux concepts and skills.
4. For those who are interested in learning Linux for web development, Codecademy offers a “Learn the Command Line” course that teaches you how to use the command line to navigate your computer and manage files. This course is great for beginners who want to understand the basics of the Linux shell.
5. No matter which course you choose, taking an introductory Linux course is a great way to familiarize yourself with this powerful operating system. Whether you’re looking to advance your career in IT or simply want to expand your knowledge, learning Linux can open up a world of possibilities.
Hands-On Linux Fundamentals Courses
| Course Name | Description | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Linux Basics | Learn the basics of Linux operating system, including file systems, command line interface, and basic shell scripting. | 4 weeks |
| Linux Administration | Gain practical skills in Linux system administration, including user management, security, and network configuration. | 6 weeks |
| Linux Shell Scripting | Learn how to automate tasks and write scripts in the Linux shell, including variables, loops, and conditional statements. | 8 weeks |