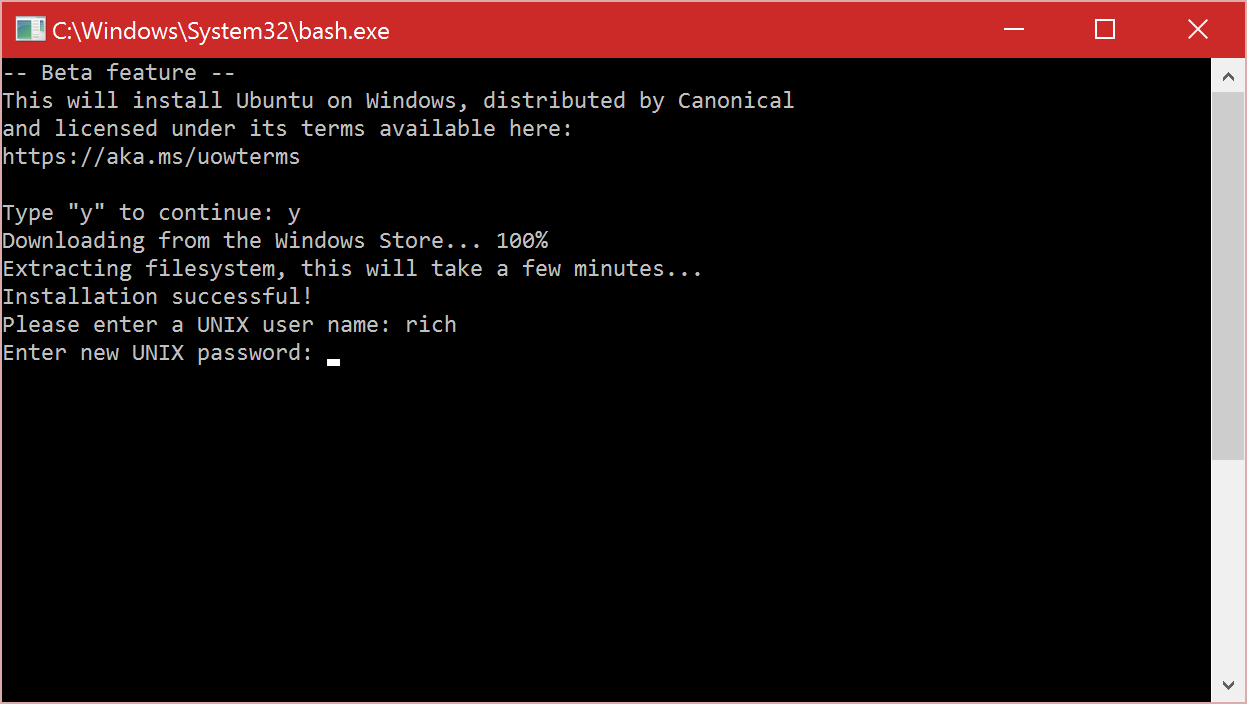
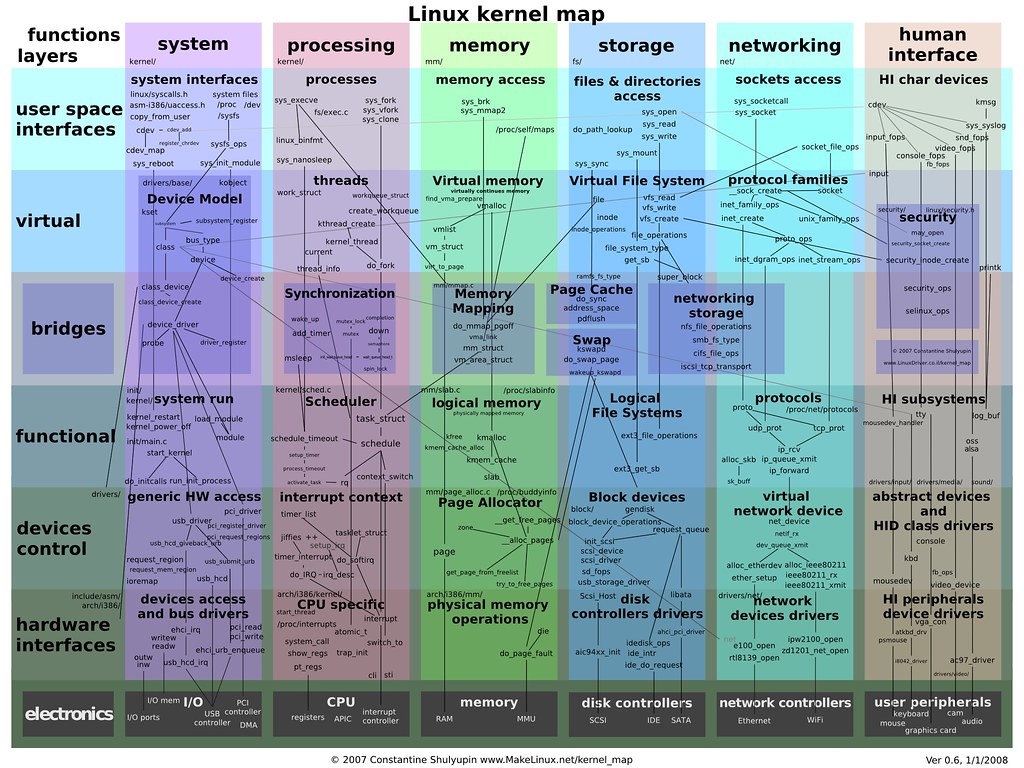
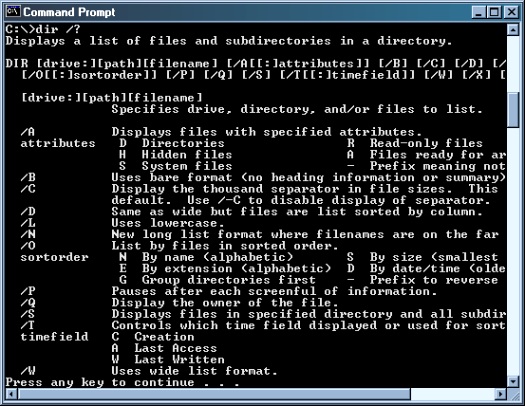
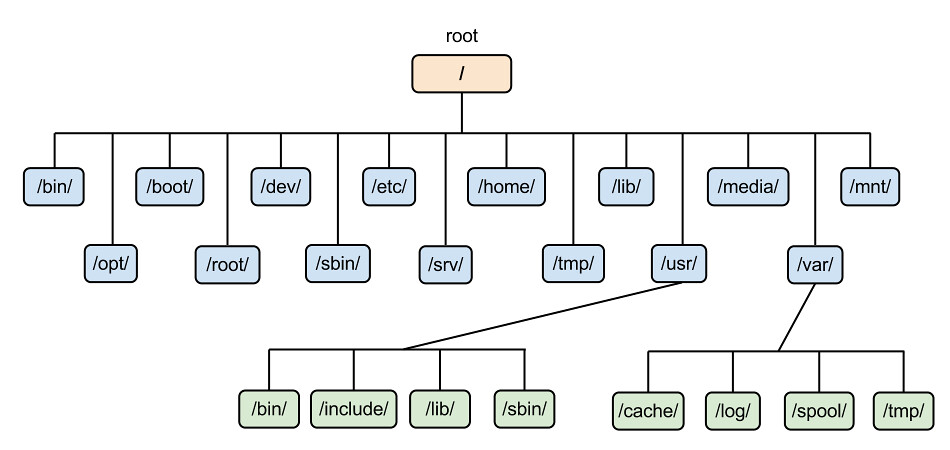
In today’s digital age, mastering the ins and outs of Linux can open up a world of possibilities and opportunities for tech enthusiasts and professionals alike.
Linux’s High Security and Stability
Linux offers high security and stability, making it a popular choice for system administrators and users looking for a reliable operating system. With Linux, you can trust that your data and systems are well-protected from cyber threats and vulnerabilities.
Its robust architecture and rock-solid stability ensure that your computer or server runs smoothly without crashes or performance issues. This is especially important for businesses and organizations that rely on their systems to be up and running at all times.
Whether you are managing a web server, database server, or cloud infrastructure, Linux provides the tools and resources needed to keep everything running efficiently. Its command-line interface allows for greater control and customization, making it a preferred choice for IT professionals and DevOps engineers.
By learning Linux, you are not only gaining valuable technical skills but also future-proofing your career. As technology continues to evolve, having knowledge of Linux will open up new opportunities in areas such as cloud computing, IoT, and cybersecurity. Start your Linux training today and take your IT skills to the next level.
Ease of Maintenance and Flexibility
The ability to customize and optimize Linux systems according to specific needs is a significant advantage, especially in the age of **cloud computing** and **Internet of things**.
Whether you’re managing a database server, a web server, or a network of computers, Linux provides the tools and support needed to streamline operations and enhance performance.
By learning Linux, individuals can future-proof their skills and stay ahead in an ever-evolving technological landscape. The knowledge gained from Linux training can open doors to new opportunities and help break free from a **dead-end job**.
Runs on Any Hardware and Is Free
| Operating System | Runs on Any Hardware | Is Free |
|---|---|---|
| Linux | Yes | Yes |
Open Source Customization and Education
Linux is widely used in system administration, web servers like Nginx, and the Internet of Things. It offers a powerful command-line interface that allows for efficient management of servers and devices.
With Linux knowledge, individuals can work with various distributions such as Ubuntu and become adept at using tools like APT for software management.
Moreover, learning Linux can future-proof one’s career by providing a solid foundation in an operating system that is widely used across different industries. It can open up opportunities in fields like DevOps and programming, making it a valuable investment in one’s professional growth.
Learning About IT Infrastructure and Networking
Learning about **IT infrastructure** and **networking** is crucial for anyone looking to pursue a career in the tech industry. Understanding how systems and networks operate is essential for roles such as **system administrator** or **network engineer**. Linux is a popular operating system used in **server** environments and learning it can open up a world of opportunities for IT professionals.
One of the key benefits of learning Linux is its widespread use in the industry. Many **servers** run on Linux, including popular web servers like **Nginx**. Having Linux skills can make you an attractive candidate for **companies** looking for professionals with expertise in this area. Additionally, Linux is known for its security and stability, making it a reliable choice for **infrastructure** and networking needs.
By learning Linux, you can also gain valuable experience working with the **command line interface** (CLI) instead of relying solely on a **graphical user interface** (GUI). This can enhance your problem-solving skills and make you more proficient in managing **servers**. Linux also has a robust package management system called **APT**, which allows users to easily install and update software.
Career Choices and Salary Trends in Linux
Learning Linux opens up a wide range of **career choices** in the tech industry, with roles such as **system administrator** and **programmer** in high demand. As more companies rely on Linux for their servers and **computers**, the job market for Linux professionals continues to grow.
One of the major benefits of pursuing a career in Linux is the **salary trends** associated with these roles. Linux professionals tend to earn higher salaries compared to those in other IT fields, making it a lucrative career choice for many.
By gaining expertise in Linux, individuals can also enhance their **job security** and future-proof their career. With the increasing popularity of Linux in various devices such as **smartphones** and **smartwatches**, the demand for skilled Linux professionals is only expected to rise.
Moreover, learning Linux can also open up opportunities to work in **developed countries** such as **Germany** and **China**, where knowledge of Linux is highly valued.
Diversity and Fun in Learning Linux
Learning Linux offers a diverse and fun experience for individuals looking to expand their knowledge of operating systems. With Linux, users can customize their system to suit their needs and preferences, making the learning process engaging and enjoyable.
By delving into the world of Linux, individuals can gain valuable skills that can be applied in various professional settings. Understanding Linux can open up new career opportunities in fields such as IT, web development, and programming.
Additionally, learning Linux allows individuals to become more proficient in using the command line interface, which can be a valuable skill when working with servers and other computing systems.