Welcome to the world of DevSecOps, where the fusion of development, security, and operations has revolutionized the way software is built and protected. In this article, we delve into the essence of DevSecOps, uncovering its principles, benefits, and how it reshapes the future of the tech industry. So, let’s embark on this enlightening journey to understand the incredible power of DevSecOps!
Understanding DevSecOps

DevSecOps is a software development approach that combines security practices with DevOps principles. It aims to integrate security into every phase of the software development life cycle, from design to deployment. By doing so, it helps organizations build secure and reliable software systems.
In traditional software development processes, security is often an afterthought. It is typically addressed towards the end of the development cycle, leading to vulnerabilities and security flaws. DevSecOps, on the other hand, emphasizes the importance of security from the very beginning.
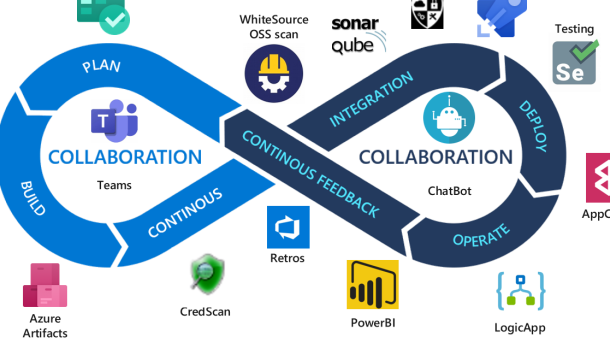
One of the key principles of DevSecOps is automation. By automating security tasks, such as vulnerability scanning and code analysis, developers can identify and fix security issues early on. This not only saves time but also reduces the risk of security breaches.
Another important aspect of DevSecOps is collaboration. It encourages close collaboration between developers, security teams, and operations teams. This collaboration ensures that security requirements are understood and implemented throughout the software development process.
DevSecOps also promotes continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD). With CI/CD, developers can continuously integrate code changes, run tests, and deploy software updates. This allows for faster and more frequent software releases, while still maintaining security and quality.
In addition to automation and collaboration, visibility is also a key component of DevSecOps. By having visibility into the software development process, organizations can identify potential security risks and take necessary actions to mitigate them. This includes monitoring the software supply chain, conducting security audits, and implementing security controls.
DevSecOps also promotes the use of open-source software and frameworks. Open-source software allows organizations to leverage existing tools and resources, saving time and effort. It also encourages collaboration and innovation within the developer community.
By adopting DevSecOps practices, organizations can create a culture of security and innovation. It helps break down silos between different teams and promotes a shared responsibility for security. This approach also helps organizations meet regulatory compliance requirements and protect against cyber threats such as malware and ransomware attacks.
Exploring the Relationship Between DevOps and Security

DevSecOps is a term that combines the principles of DevOps and security to create a more secure software development process. It emphasizes the importance of integrating security practices throughout the entire software development life cycle, rather than treating it as an afterthought.
One of the key benefits of DevSecOps is that it allows for continuous integration and continuous delivery, enabling software to be developed and deployed at a faster pace. With traditional software development processes, security often takes a backseat to speed and functionality. However, with DevSecOps, security is built into the development pipeline from the very beginning, ensuring that vulnerabilities and risks are addressed early on.
To achieve this, DevSecOps relies on a combination of tools, practices, and cultural changes. Version control and automation are used to track and manage changes to the software code, while security controls are put in place to ensure that only authorized individuals have access to the code. Information security audits and vulnerability assessments are also conducted regularly to identify and address any security weaknesses.
In addition to these technical aspects, DevSecOps also requires a shift in organizational culture. It encourages collaboration and communication between developers, security teams, and operations teams, breaking down silos and fostering a shared responsibility for security. This culture of collaboration helps to facilitate the integration of security practices into the software development workflow.
Another important aspect of DevSecOps is the consideration of the software supply chain. Just as a physical supply chain can be vulnerable to disruptions or malicious activity, the software supply chain can also be a target for attacks. DevSecOps emphasizes the importance of assessing and securing all components of the software ecosystem, including third-party libraries and dependencies.
Tools and Skills for Successful DevSecOps Implementation

| Category |
Tools |
Skills |
| Version Control |
Git, SVN |
Version control system usage |
| Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) |
Jenkins, CircleCI, Travis CI |
Automation scripting, familiarity with CI/CD tools |
| Containerization |
Docker, Kubernetes |
Containerization concepts, container orchestration |
| Static Code Analysis |
SonarQube, ESLint |
Understanding of code quality and security vulnerabilities |
| Security Testing |
OWASP ZAP, Burp Suite |
Web application security testing, vulnerability assessment |
| Infrastructure as Code (IaC) |
Terraform, CloudFormation |
Infrastructure provisioning, configuration management |
| Security Orchestration, Automation and Response (SOAR) |
Demisto, Phantom |
Security incident response, automation workflows |
Best Practices for Supporting a DevSecOps Team
Supporting a DevSecOps team requires a focused approach to ensure the success of the team and the security of the applications they develop. Here are some best practices to consider:
1. Emphasize Continuous Learning: Encourage team members to continuously update their skills and knowledge in areas such as Linux, as it forms the foundation of many enterprise systems. Providing Linux training opportunities can help team members stay up-to-date with the latest security practices and tools.
2. Foster Collaboration: DevSecOps is all about breaking down silos and promoting collaboration between development, security, and operations teams. Create an environment that encourages open communication, knowledge sharing, and cross-functional collaboration. This can be achieved by implementing collaborative tools and fostering a culture of transparency and trust.
3. Implement Security as Code: Integrate security practices into the development process by adopting the concept of “security as code.” This involves treating security configurations, policies, and guidelines as code, which can be version-controlled, tested, and automated. By incorporating security into the development pipeline, teams can identify and address vulnerabilities early in the software development life cycle.
4. Automate Security Testing: Implement automated security testing throughout the development process to identify vulnerabilities and security weaknesses. This includes static code analysis, dynamic application security testing, and software composition analysis. By automating these tests, teams can quickly identify and address security issues, reducing the risk of security breaches.
5. Conduct Regular Security Audits: Regularly assess the security posture of your applications and infrastructure through comprehensive security audits. These audits should cover areas such as access controls, vulnerability management, patching, and incident response. By conducting regular audits, you can identify potential weaknesses and take proactive steps to mitigate risks.
6. Prioritize Application Security: DevSecOps teams should prioritize application security throughout the software development life cycle. This includes incorporating security requirements into the design phase, conducting secure coding practices, and performing thorough security testing before deployment. By prioritizing application security, teams can reduce the likelihood of security incidents and protect sensitive data.
7. Establish Feedback Loops: Create feedback loops between development, security, and operations teams to ensure continuous improvement. Encourage regular meetings, retrospectives, and post-mortems to identify areas for improvement and address any issues or concerns. This iterative approach allows teams to learn from past experiences and make necessary adjustments to enhance security practices.
8. Stay Abreast of Emerging Threats: Stay informed about the latest security threats, vulnerabilities, and industry best practices. Regularly monitor security news, attend industry conferences, and engage with the security community to stay ahead of potential risks. By staying informed, teams can proactively address emerging threats and adapt their security practices accordingly.
Supporting a DevSecOps team requires a combination of technical expertise, collaboration, and a proactive approach to security.